Our capabilities and experience
Read more about how we help manage complex clinical research across many therapeutic areas worldwide.
Page 1 of 6
mRNA Report
mRNA technology has the potential to address diseases globally that have not had effective vaccines nor treatments to date. Read this report to learn about the promise of mRNA to prevent and treat endemic diseases in resource-limited areas with the populations who would benefit the most.
ClinConvos, Episode 5: Sienneh Tamba Discusses the Importance of Regulatory Compliance
ClinConvos is FHI Clinical’s platform for conversations with our leaders in the clinical research industry. In this episode of ClinConvos, Sienneh Tamba, Regulatory Compliance and Ethics Assistant, discusses the functions of the Regulatory Compliance department with Joseph Cooper, Clinical Communications Coordinator.
ClinConvos, Episode 4: Claudia Christian and Leonard Herbst Discuss FHI Clinical’s Growth
ClinConvos is FHI Clinical’s platform for conversations with our leaders in the clinical research industry. In this episode, Claudia Christian, VP, Client Solutions, and Leonard Herbst, Global Head, Clinical Affairs, discuss FHI Clinical’s growth since its acquisition of TCD Global in South Africa.
ClinConvos, Episode 3: 40+ Years and Still no HIV Vaccine: Has Patience Been a Virtue?
ClinConvos is FHI Clinical’s platform for conversations with our leaders in the clinical research industry. The development of an HIV vaccine has been marked by both long-standing and emerging challenges and opportunities. In this video, Sanchia Theron, Global Head, Medical Affairs, and Andy Fleming, Senior Account Development Manager, discuss major takeaways from our roundtable discussion at World Vaccine Congress Washington: 40+ Years and Still no HIV Vaccine: Has Patience Been a Virtue?
Our Clinical Trial Experience With Tuberculosis
The FHI Clinical project team has partnered with companies to conduct clinical trials as well as epidemiological and observational studies for tuberculosis in 30 countries worldwide.
ClinConvos, Episode 2: Abraham Van Wyk on Why to Conduct Clinical Trials in Africa
ClinConvos is FHI Clinical’s platform for conversations with our leaders in the clinical research industry. In this episode, Abraham Van Wyk, Managing Director, South Africa, and Hayley Jones, Clinical Project Manager, discuss the advantages of conducting clinical trials in Africa and particularly with FHI Clinical.
ClinConvos, Episode 1: Craig McNees Asks Rob King “Why FHI Clinical?”
ClinConvos is FHI Clinical’s platform for conversations with our leaders in the clinical research industry. In this first episode, Craig McNees, Senior Director, Client Solutions, asks Rob King, COO, “Why FHI Clinical?”
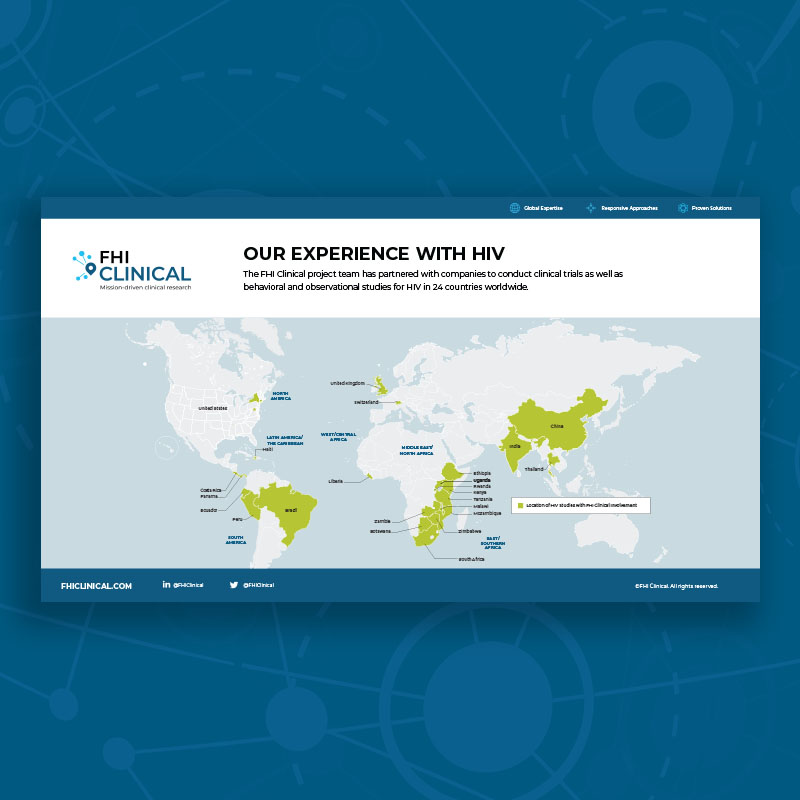
Our Clinical Trial Experience With HIV
The FHI Clinical project team has partnered with companies to conduct clinical trials as well as behavioral and observational studies for HIV in 24 countries worldwide.
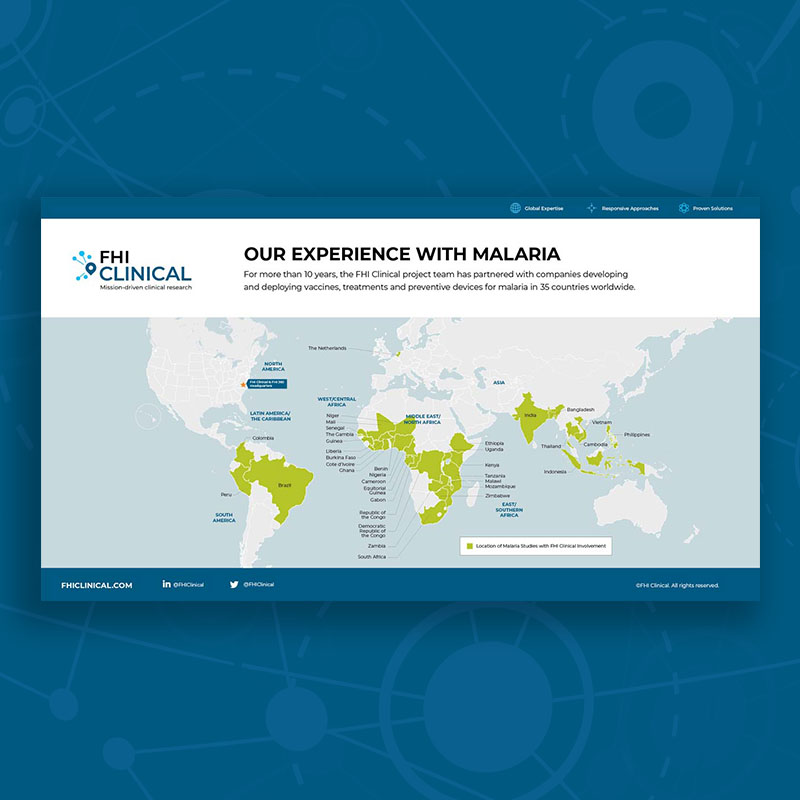
Our Clinical Trial Experience With Malaria
For nearly 20 years, the FHI Clinical project team has partnered with companies developing and deploying vaccines, treatments and preventive devices for malaria in 38 countries worldwide.
Our Experience in sub-Saharan Africa
FHI Clinical has long-standing relationships, a local team and broad expertise in sub-Saharan Africa. We’re ready to help you confidently expand your research across the region, finding the best-fit countries and populations for your target indication and study type.